1. 역할
1) DAG의 노드가 되는 특정 유형의 작업을 생성할 수 있도록 함
2) 모든 Operator는 Base Operator 에서 상속되어 생성됨
3) 모든 Sensor 는 Base Sensor Operator에서 상속되어 생성됨
4) 모든 Sensors는 Base Sensor Opeatior의 timeout과 poke_interval 을 상속함
5) 연산자는 3가지 유형을 가짐
(1) 작업을 수행하거나 다른 시스템에 작업을 수행하도록 하는 지시하는 Action Operator
(2) 한 시스템에서 다른 시스템으로 데이터를 이동 시키는 Transfer Operator
(3) 특정 조건이 충족될 때까지 반복으로 실행되는 Sensor Operator
2. packages
1) airflow.operators
(1) providers 패키지가 추가됨으로써 2.0에 남은 패키지만 설명
(2) airflow.operators.bash
I. Bash Shell Script를 실행하는 Operator
II. Syntax
class airflow.operators.bash.BashOperator(*,
bash_command: str,
env: Optional[Dict[str, str]] = None,
output_encoding: str = 'utf-8',
**kwargs)
III. Parameters
A. bash_command(str) : bash Shell Script
B. env(dict) : 기본 값은 none 이나 사용될 경우 dict 형태의 환경변수 선언하는 내용을 기술
C. output_encoding(str) : bash_command의 출력값 인코딩
IV. example
bash_task = BashOperator(
task_id="bash_task",
bash_command='echo "here is the message: \'$message\'"',
env={'message': '{{ dag_run.conf["message"] if dag_run else "" }}'},
output_encoding='utf-8',
)
(3) airflow.operators.branch
I. 분기를 설정하는 Operator, 설정 method와 실행 method로 나뉨
II. choose_branch : 분기를 설정하는 method
A. Syntax
class airflow.operators.branch.BaseBranchOperator.choose_branch(self, context: Dict)
III. execute : 실행하는 method
A. Syntax
class airflow.operators.branch.BaseBranchOperator.execute(self, context: Dict)
IV. Parameters
A. context (dict) : 분기를 진행하기 원하는 정보
V. example
options = ['branch_a', 'branch_b', 'branch_c', 'branch_d']
branching = BranchPythonOperator(
task_id='branching',
python_callable=lambda: random.choice(options),
)
(4) airflow.operators.dummy
I. 아무 작업도 하지 않는 연산자로 여러 다른 작업들을 그룹화 하는데 사용
II. Syntax
class airflow.operators.dummy.DummyOperator(**kwargs)
III. example
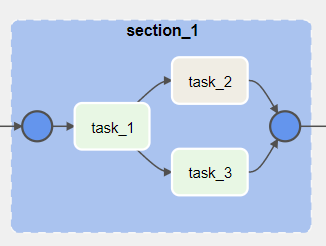
with TaskGroup("section_1", tooltip="Tasks for section_1") as section_1:
task_1 = DummyOperator(task_id="task_1")
task_2 = BashOperator(task_id="task_2", bash_command='echo 1')
task_3 = DummyOperator(task_id="task_3")
(5) airflow.operators.email
I. 이메일 발송
II. Syntax
class airflow.operators.email.EmailOperator(*, to: Union[List[str], str],
subject: str,
html_content: str,
files: Optional[List] = None,
cc: Optional[Union[List[str], str]] = None,
bcc: Optional[Union[List[str], str]] = None,
mime_subtype: str = 'mixed',
mime_charset: str = 'utf-8',
conn_id: Optional[str] = None, **kwargs)
III. Parameters
A. to(str or list[str]) : 받는 사람
B. subject(str) : 제목
C. html_content(str) : 이메일에 html 요소 사용 여부
D. files(list) : 이메일에 첨부된 파일 이름
E. cc(str or list[str]) : 참조
F. bcc(str or list[str]) : 숨겨진 참조
G. mime_subtype(str) : MIME 하위 컨텐츠 타입
가) text/plain : 단순 텍스트
나) multipart/mixed : 첨부된 내용이 있는 메시지
다) multipart/alternative : html과 다른 포맷을 함께 보낸 메시지
H. mime_charset : Content-Type 해더의 Charset
IV. example
email = EmailOperator(
task_id='send_email',
to='to@gmail.com',
subject='Airflow Alert',
html_content=""" <h3>Email Test</h3> """,
dag=dag
)
(6) airflow.operators.generic_transfer
I. Source에서 Destination 으로 데이터를 복사 한다.
II. Syntax
class airflow.operators.generic_transfer.GenericTransfer(*, sql: str,
destination_table: str,
source_conn_id: str,
destination_conn_id: str,
preoperator: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None, **kwargs)
III. Parameters
A. sql (str) : SQL 쿼리
B. destination_table (str) : 저장될 곳의 tablea명
C. source_conn_id (str) : Source 연결 정보
D. destination_conn_id (str) : destination 연결 정보
E. preoperator (str or list[str]) : 복사 실행 전 실행된 SQL문
IV. example
sql = "SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES LIMIT 100;"
t = operators.generic_transfer.GenericTransfer(
task_id='test_m2m',
preoperator=[
"DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test_mysql_to_mysql",
"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "
"test_mysql_to_mysql LIKE INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES"
],
source_conn_id='airflow_db',
destination_conn_id='airflow_db',
destination_table="test_mysql_to_mysql",
sql=sql,
dag=self.dag)
(7) airflow.operators.latest_only
I. airflow의 Task는 선언된 schedule에 의해 실행되는데 시작 날짜 이후 실행된 log가 없다면 최신 날짜까지 모두 실행되기도 한다.(backfill) 이때 해당 operator는 가장 최근 일만 실행되도록 한다.
II. Syntax
class airflow.operators.latest_only.LatestOnlyOperator
III. example
latest_only = LatestOnlyOperator(task_id='latest_only', dag=dag)
task1 = DummyOperator(task_id='task1', dag=dag)
task1.set_upstream(latest_only)
(8) airflow.operators.python
I. Python Source를 실행하기 위한 Operator
II. PythonOperator
A. Python을 실행
B. Syntax
class airflow.operators.python.PythonOperator(*, python_callable: Callable,
op_args: Optional[List] = None,
op_kwargs: Optional[Dict] = None,
templates_dict: Optional[Dict] = None,
templates_exts: Optional[List[str]] = None, **kwargs)
C. Parameters
가) python_callable (python callable) : 호출할 Python 개채
나) op_kwargs (dict) : python 개체 함수에 들어갈 키워드와 인수 정보
다) op_args (dict) : python 개체 함수에 들어갈 인수 정보
D. example
def my_sleeping_function(random_base):
"""This is a function that will run within the DAG execution"""
time.sleep(random_base)
# Generate 5 sleeping tasks, sleeping from 0.0 to 0.4 seconds respectively
for i in range(5):
task = PythonOperator(
task_id='sleep_for_' + str(i),
python_callable=my_sleeping_function,
op_kwargs={'random_base': float(i) / 10},
)
III. BranchPythonOperator
A. Python 함수를 통해 분기
B. Syntax
class airflow.operators.python.BranchPythonOperator
C. example
def which_path():
'''
return the task_id which to be executed
'''
if True:
task_id = 'path_A'
else:
task_id = 'path_B'
return task_id
check_situation = BranchPythonOperator(
task_id='check_situation',
python_callable=which_path,
dag=dag,
)
IV. ShortCircuitOperator
A. bool 조건에 맞을 때만 실행
B. Syntax
class airflow.operators.python.ShortCircuitOperator
C. example
cond_true = ShortCircuitOperator(
task_id='condition_is_True',
python_callable=lambda: True,
)
ds_true = [DummyOperator(task_id='true_' + str(i)) for i in [1, 2]]
chain(cond_true, *ds_true)
V. PythonVirtualenvOperator
A. Python 가상 환경에서 실행
B. Syntax
class airflow.operators.python.PythonVirtualenvOperator(*, python_callable: Callable,
requirements: Optional[Iterable[str]] = None,
python_version: Optional[Union[str, int, float]] = None,
use_dill: bool = False,
system_site_packages: bool = True,
op_args: Optional[List] = None,
op_kwargs: Optional[Dict] = None,
string_args: Optional[Iterable[str]] = None,
templates_dict: Optional[Dict] = None,
templates_exts: Optional[List[str]] = None, **kwargs)
C. Parameter
가) python_callale (function) : 외부 변수가 사용되지 않은 python 함수
나) requirement (list[str]) : 환경 구성(pip install command)
다) op_kwargs (dict) : python 개체 함수에 들어갈 키워드와 인수 정보
라) op_args (dict) : python 개체 함수에 들어갈 인수 정보
D. example
def callable_virtualenv():
"""
Example function that will be performed in a virtual environment.
Importing at the module level ensures that it will not attempt to import the
library before it is installed.
"""
from time import sleep
from colorama import Back, Fore, Style
print(Fore.RED + 'some red text')
print(Back.GREEN + 'and with a green background')
print(Style.DIM + 'and in dim text')
print(Style.RESET_ALL)
for _ in range(10):
print(Style.DIM + 'Please wait...', flush=True)
sleep(10)
print('Finished')
virtualenv_task = PythonVirtualenvOperator(
task_id="virtualenv_python",
python_callable=callable_virtualenv,
requirements=["colorama==0.4.0"],
system_site_packages=False,
)
(9) airflow.operators.sql
I. SQL 구문을 실행
II. BaseSQLOperator
A. DB연결 hook을 리턴 (hook - 부 플랫폼, 데이터베이스에 접근할 수 있도록 만든 인터페이스)
B. Syntax
class airflow.operators.sql.BaseSQLOperator(*, conn_id: Optional[str] = None,
database: Optional[str] = None, **kwargs)
C. Parameter
가) conn_id (str) : DB 연결 정보
나) database (str) : 연결할 Database 명
III. SQLCheckOperator
A. SQL 쿼리를 실행하고 응답에서 단일 행을 수신할 것으로 예상하고 행의 모든 값을 Bool로 캐스팅하려고 시도
B. Syntax
class airflow.operators.sql.SQLCheckOperator(*, sql: str, conn_id: Optional[str] = None,
database: Optional[str] = None, **kwargs)
C. Parameter
가) sql (str) : 단일 행 반환 SQL 쿼리
나) conn_id (str) : DB 연결 정보
다) database (str) : 연결할 Database 명
D. example
operator = SQLCheckOperator(
sql="SELECT COUNT(*) FROM some_table WHERE some_column='{{ yesterday_ds_nodash }}'"
)
(10) airflow.operators.subdag
I. Dag가 SubDag로 실행되도록 함
II. Syntax
class airflow.operators.subdag.SubDagOperator(*, subdag: DAG,
session: Optional[Session] = None,
conf: Optional[Dict] = None,
propagate_skipped_state: Optional[SkippedStatePropagationOptions] = None, **kwargs)
III. Parameter
A. subdag : 해당 Dag의 Sub로 등록
B. session : sqlalchemy 세션
C. conf : Sub Dag 구성
D. propagate_skipped_state : Dag의 downstream 작업에 전파되어야 하는지 여부를 정의
IV. Example
section_1 = SubDagOperator(
task_id='section-1',
subdag=subdag(DAG_NAME, 'section-1', args),
)
(11) airflow.operators.trigger_dagrun
I. 지정된 DAG를 실행하는 트리거
II. Syntax
class airflow.operators.trigger_dagrun.TriggerDagRunOperator(*, trigger_dag_id: str,
conf: Optional[Dict] = None,
execution_date: Optional[Union[str, datetime.datetime]] = None,
reset_dag_run: bool = False,
wait_for_completion: bool = False,
poke_interval: int = 60,
allowed_states: Optional[List] = None,
failed_states: Optional[List] = None, **kwargs)
III. Parameter
A. trigger_dag_id (str) : 트리거할 dag_id
B. conf (dict) : dag 실행에 대한 구성
C. execution_date (str or datetime.datetime) : 실행할 날짜
D. reset_dag_run (bool) : 이미 실행되고 있는 dag라면 기존의 실행을 지우고 재실행을 하는지 여부
E. wait_for_completion (bool) : 이전 dag의 실행완료를 기다릴지 여부
F. poke_interval (int) : wait_for_completion=True일 때 dag 실행 상태를 확인하기 위한 interval
IV. Example
trigger = TriggerDagRunOperator(
task_id="test_trigger_dagrun",
trigger_dag_id="example_trigger_target_dag",
conf={"message": "Hello World"},
)
3. 출처
1) https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/_api/airflow/operators/index.html
2) https://stackoverflow.com/questions/51829200/how-to-set-up-airflow-send-email
3) https://programtalk.com/python-examples/airflow.operators.generic_transfer.GenericTransfer/
4) https://getchan.github.io/data/airflow_2/
5) https://moons08.github.io/programming/airflow-branch/
6) https://www.mikulskibartosz.name/data-quality-checks-using-sqlcheckoperator/
'BigData > Dataflow' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Airflow - 간단한 Mysql to MSSQL(SQL Server) 이관 예제 (2) | 2021.06.16 |
|---|---|
| Airflow 병렬 프로세스 및 설치 (0) | 2021.05.17 |
| Airflow 기초 설치 (0) | 2021.04.27 |







최근댓글